Thoughts behind sustainability management and its framework
We believe a business should create value for society through its key practices.
We are committed to sustainably increasing our long-term value by putting Our Mission and Values into practice.
OMRON's reason for being is to create social value through business and continue to contribute to the development of society. To achieve this, we believe it is important for OMRON to identify material sustainability issues on which to focus, incorporate them into our medium-term and long-term strategies, set specific initiatives and targets, and implement them through our business. For OMRON, sustainability means pursuing both social and corporate sustainability. By fully integrating our key sustainability issues with our Long-Term Vision and Medium-Term Management plan, we will continue to strive for the sustainable development of society and the sustainable growth of OMRON.
The OMRON Group has established a company-wide management structure to implement sustainability initiatives on a global basis. The status of initiatives to address material sustainability issues is regularly reported to the Executive Council, where progress status and issues are discussed.
In fiscal 2023, we appointed Directors in charge of the environment and human rights to strengthen the monitoring and supervision roles of the Board of Directors for sustainability initiatives.
We also appointed the Sustainability Executive Officer, who has operational responsibility of promoting sustainability, with the aim of further strengthening sustainability governance for the entire Group.
In addition, we established the Environment Steering Committee and the Human Rights Steering Committee directly under the Sustainability Committee. Chaired by the Sustainable Executive Officer, the Committee members discuss and make decisions on how to address material sustainability issues on a first-line, practical basis and to monitor the progress of fiscal year plans. To the Committees, Directors in charge of the environment and human rights respectively attend as observers. In addition, Regional Sustainability Committees were established in each area to strengthen efforts focused on issues specific to each area.
From fiscal 2024, with a view to further strengthening sustainability initiatives on a practical operating basis, the Sustainability Office, which was previously positioned under the direct supervision of the Board of Directors, has been dissolved to enhance the organization for this purpose. Instead, we established the Sustainability Management Department as an operating division under the Global Corporate Communications & Engagement HQ.
These sustainability initiatives are regularly reported to the Board of Directors to further strengthen governance throughout the Group.
Since fiscal 2017, a sustainability evaluation based on the Dow Jones Sustainability Indices (DJSI) has been incorporated into the evaluation for medium- to long-term performance-linked compensation (stock compensation) for officers. In addition, the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and the score of Sustainable Engagement Index (SEI) in an engagement survey for employees were newly added as a KPI that contributes to OMRON’s growth when the officer compensation system was revised in fiscal 2020. The adoption of third-party sustainability evaluation enhances fairness and transparency, and the disclosure of sustainability policies, targets, KPIs, and progress on the website and others enhances dialogue with stakeholders in order to evolve the initiatives.

We determined our material sustainability issues through a series of discussions amongst our management teams, based on suggestions from internal discussions and those with outside experts. This process has a key focus on the following three ideas. We proactively disclose information to our stakeholders and engage in responsible dialogue with them regarding our progress in achieving targets related to material sustainability issues, in accordance with our Sustainability Policy.
STEP 1
Exploring the Long-Term Vision
Utilizing practice of our Management Philosophy, our management compass, and backcasting from a society envisioned for 2030 and beyond to identify factors of social change that affect the sustainable development of society and the Company, and to explore the direction of our Long-Term Vision
STEP 2
Organizing Focus Points
Based on the direction of our next Long-Term Vision, organizing focus points in identifying material sustainability issues
STEP 3
Hypothesizing Material Sustainability Issues
Hypothesizing material sustainability issues along the following two axes:
STEP 4
Discussion at Management Level
Frequent discussions at the Executive Council, chaired by the CEO and attended by Executive Officers
STEP 5
Dialogue with Stakeholders
Based on hypotheses, holding dialogues with institutional investors, experts, NPOs, etc. to confirm their expectations and demands on the Group and identify material sustainability issues
STEP 6
Set Long-Term and Medium-Term Goals
Formulating long-term and medium-term business and operational strategies and setting long-term and medium-term targets based on material sustainability issues
STEP 7
Discussion and Approval at Management Level
Deliberation and approval by the Board of Directors after discussions at the Executive Council, chaired by the CEO and attended by Executive Officers
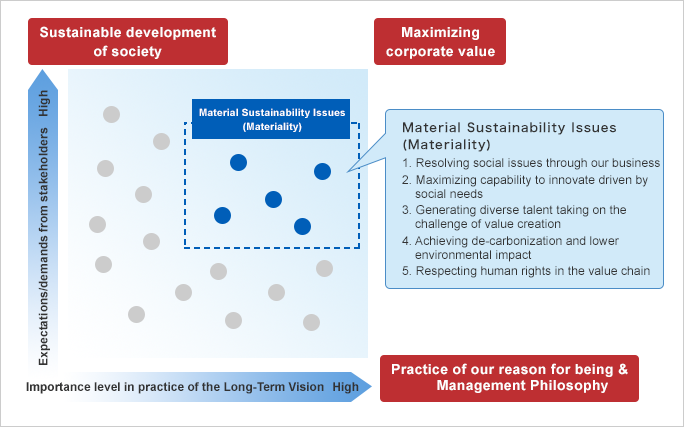
We identified five key sustainability issues that we judged to be particularly important for the sustainable development of society after assessing and confirming the expectations and requests of various stakeholders, including external evaluation organizations, our shareholders, including institutional and individual investors, customers, local communities, and NPO/NGOs.
We at the OMRON Group have identified material sustainability issues, and incorporated them for the first time into our Long-Term Vision. Under SF2030, we aim to address the following five material issues.
Under SF2030, OMRON is evolving and promoting integrated initiatives to business growth and sustainability issues. The creation of social and economic value is realized through the aim of “solving social issues through business.” In order to achieve this, it is essential to create new businesses by innovation driven by social needs and to develop diverse human resources to support these new businesses. These will also lead to “OMRON’s sustainable growth.” In addition, decarbonization, reduction of environmental impact, and respect for human rights in the value chain have become essential corporate social responsibilities to promote the “sustainable development of society.” By addressing these five key sustainability issues, SF2030 aims to maximize corporate value by creating both social and economic value.
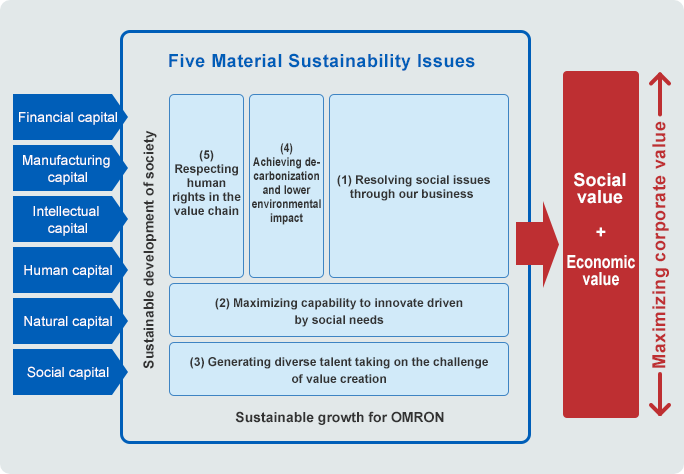
Furthermore, because the material sustainability issues were identified to achieve OMRON's long-term vision, the PDCA cycle for sustainability issues is incorporated in our Integrated Risk Management system.
The degree of achievement of the medium-term targets for materiality issues is partly linked to the stock compensation of Directors (excluding Outside Directors), and Executive Officers.
| Material sustainability issues | Medium-term targets (FY2024 targets) | Long-term goals (SF2030 targets) |
|---|---|---|
| ① Resolving social issues through our business |
|
|
| ② Maximizing capability to innovate driven by social needs |
|
|
| ③ Generating diverse talent taking on the challenge of value creation |
|
|
| ④ Achieving de-carbonization and lower environmental impact |
|
|
| ⑤ Respecting human rights in the value chain |
|
|